If you’re trading crypto without looking at the order book, you’re basically guessing. The book shows you what buyers and sellers are really doing, right now. Want better entries, cleaner exits, and fewer surprises? Learn how to read the signals that most beginners miss. It’s easier than it looks, and way more useful than you think.
What Is an Order Book in Crypto Trading?
An order book is a live list of all pending buy and sell orders for a particular asset on a crypto exchange. It shows the specific price and amount traders want for each order, organizing real-time supply and demand.
The order book data is split into two sides: bids (buy) and asks (sell). Each bid or ask is grouped by specified price and volume. When a buyer and seller match at the same price, the order is filled and removed.
Every order book snapshot reflects a single trading pair—like BTC/USDT—and only displays orders for that pair. Since each exchange and pair has its own flow, prices can differ slightly between different cryptocurrencies and platforms.

How an Order Book Functions in Real Time
An order book updates in real time, when each new order—buy or sell—is added based on price. When the highest bid meets the lowest ask, the trade executes instantly. That order then disappears from the book.
This live stream of real time market data lets the order book reflect ongoing activity. The top prices—best bid and best ask—keep shifting as orders fill, which constantly redefines the current market price.
Only limit orders appear on the book. Market orders don’t, since they execute immediately at available prices. That’s why the visible data represents trader intentions, not completed trades.
As market conditions change, the depth and shape of the book adjusts. A deeper book signals high market liquidity, while thin depth shows fragility.
Anatomy of an Order Book
A crypto order book may look complex at first, but it’s composed of a few fundamental parts that are consistent across exchanges.
Bids (Buy Orders): What They Mean
Buy orders, or bids, are offers from traders looking to purchase crypto at a specific price. Each bid includes the price and quantity. The highest bid is at the top of the buy side, it’s the most someone is willing to pay now. Together, these bids reflect market participants’ demand and where buyers expect support.
Asks (Sell Orders): What They Represent
Sell orders, or asks, are from traders aiming to sell crypto at a chosen price. Each includes an asking price and volume. The lowest ask—at the top of the sell side—is the cheapest current offer. Asks show where market participants want to take profit and represent the available supply in the market.
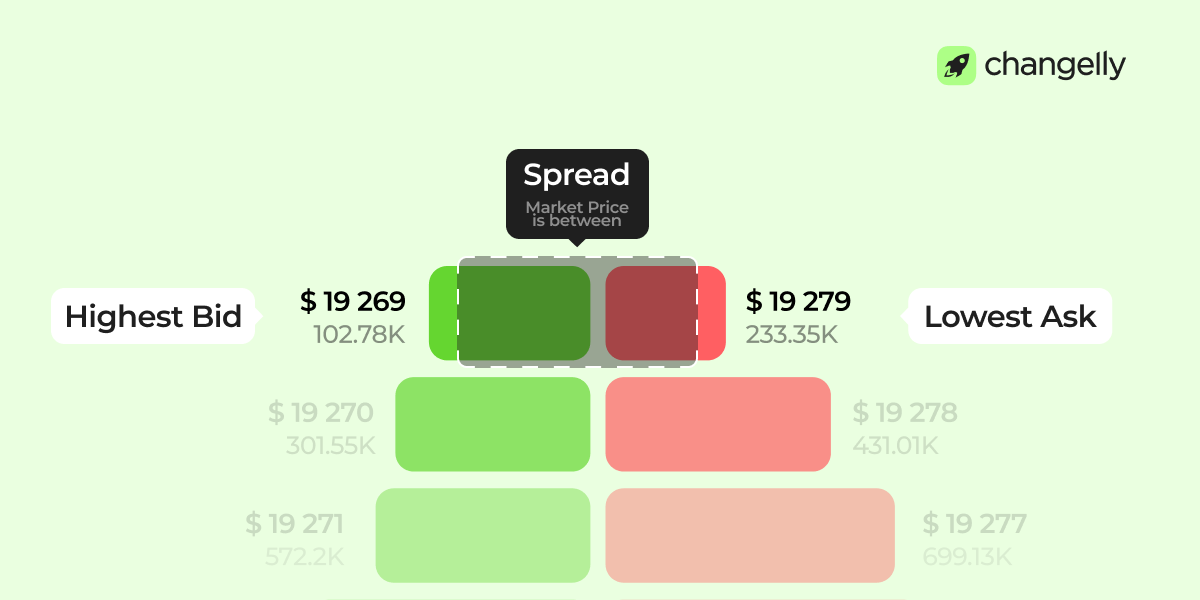
Bid-Ask Spread: Why It Matters
The spread is the gap between the best bid and the lowest ask. A small spread means active trading and good liquidity. A large spread suggests low activity or uncertainty. The spread is where market makers profit, and where price discovery happens. It helps define the real market price and the best price for immediate execution.
Order Quantity: How Much Crypto Is Being Traded
Order quantity shows how much crypto is listed at each price level. Larger volumes suggest stronger buyer or seller interest. If many units sit at a level, that price may act as support or resistance. This data helps with liquidity analysis—more volume means greater market depth and better market liquidity for large trades.
Price Levels: Stacking Orders by Price
Each price level shows all orders at a specific price. Exchanges group identical price points into one line. The more stacked levels, the deeper the order book depth and stability.
Time Priority: Why Older Orders Might Get Filled First
Orders at the same price follow time priority, meaning older orders fill first. This ensures fairness among market participants. The order book data tracks submission time for proper matching.
How Do Order Books Work?
Here’s how order books work: each time a trader places a buy or sell order, it’s added to the book at their chosen price. When a market participant submits a matching order—say, a buy at the same price as a sell—the matching engine executes the trade instantly and removes both orders. This matching system ensures fast execution and helps determine the real-time market price through price discovery. The top bid and ask constantly update as trades occur.
Market makers play a key role here. They place both buy and sell orders to provide liquidity, profit from the bid-ask spread, and stabilize the market.
When prices differ between exchanges, traders look for arbitrage opportunities. By buying low on one platform and selling high on another, they profit from the gap. These trades help balance prices across markets and keep the crypto ecosystem more efficient.

How to Get Free Crypto
Simple tricks to build a profitable portfolio at zero cost

How to Read an Order Book
Typical Order Book Layout: Columns and Rows
Most crypto platforms display buy and sell orders in two columns: buys and sells. Each row shows a price and amount. The top of the book highlights the best price where the next trade might happen.
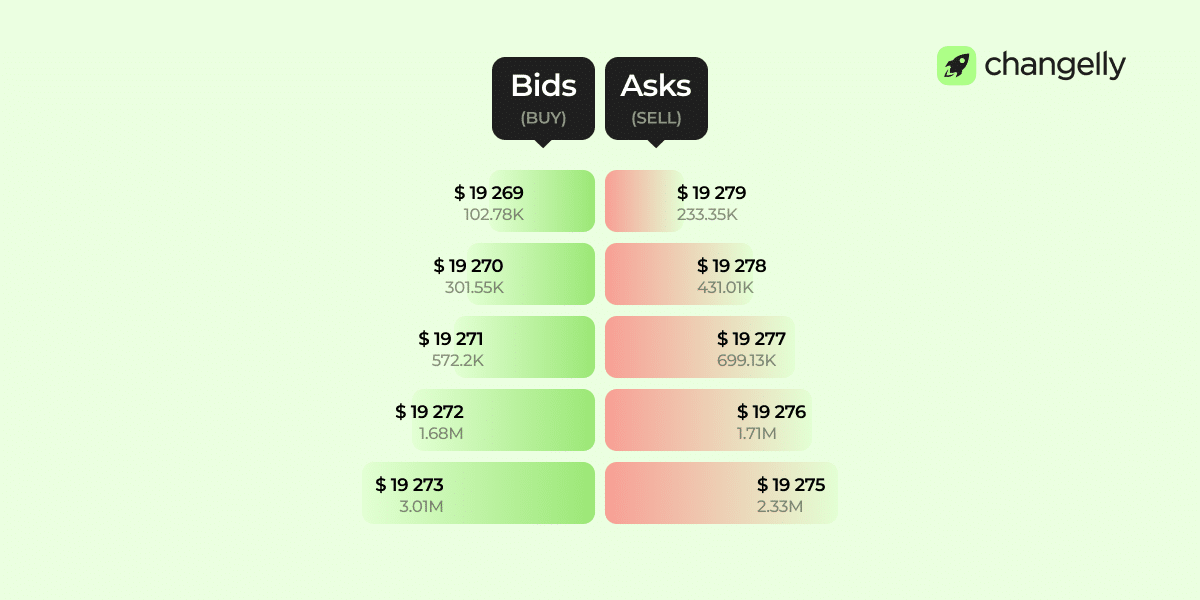
Colour Coding: Green (Buy) vs. Red (Sell)
Green highlights buy orders (bids); red shows sell orders (asks). These colors help you quickly scan the order book and spot the balance between buyer demand and seller pressure.
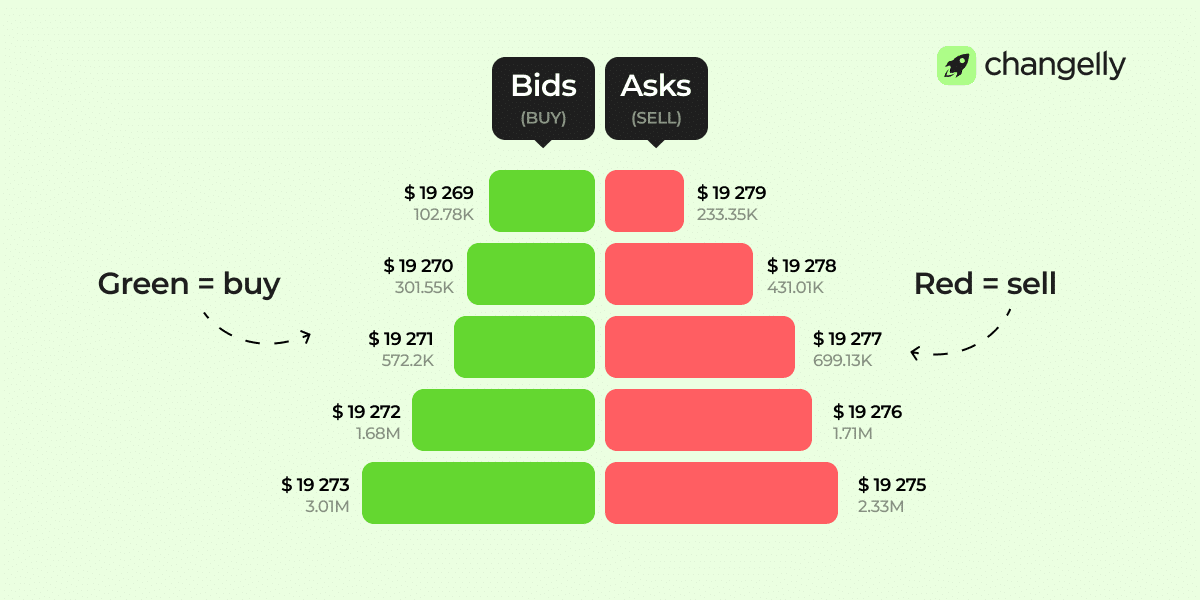
How to Find the Market Price Using the Order Book
The current market price is between the highest bid and the lowest ask. This gap is the spread. When you place a market order, it fills at the best price available from the other side.
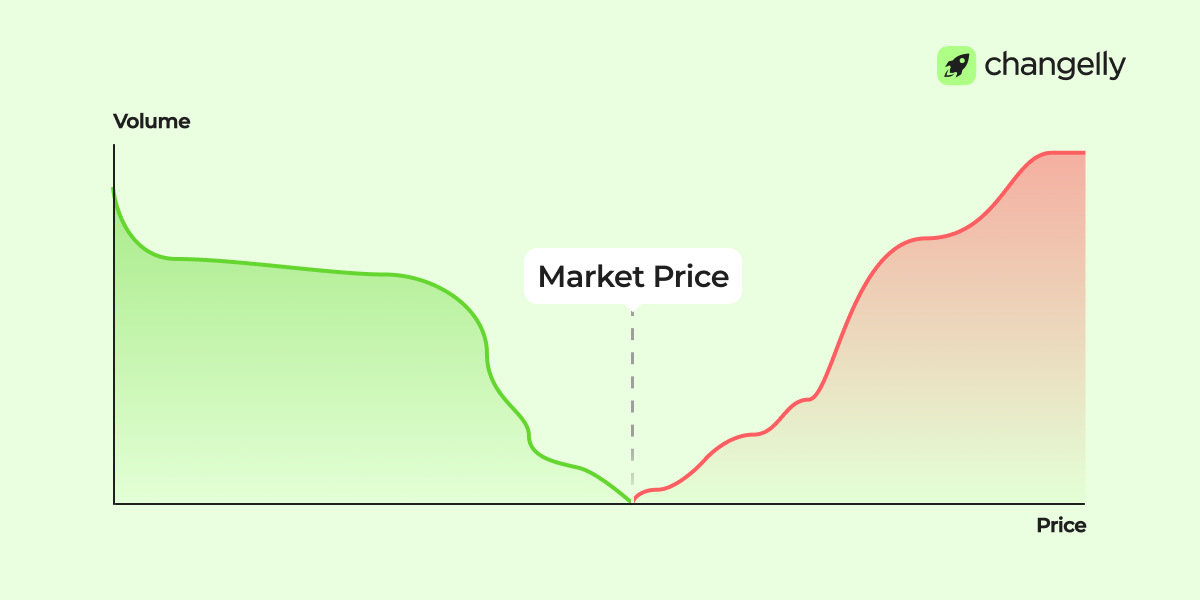
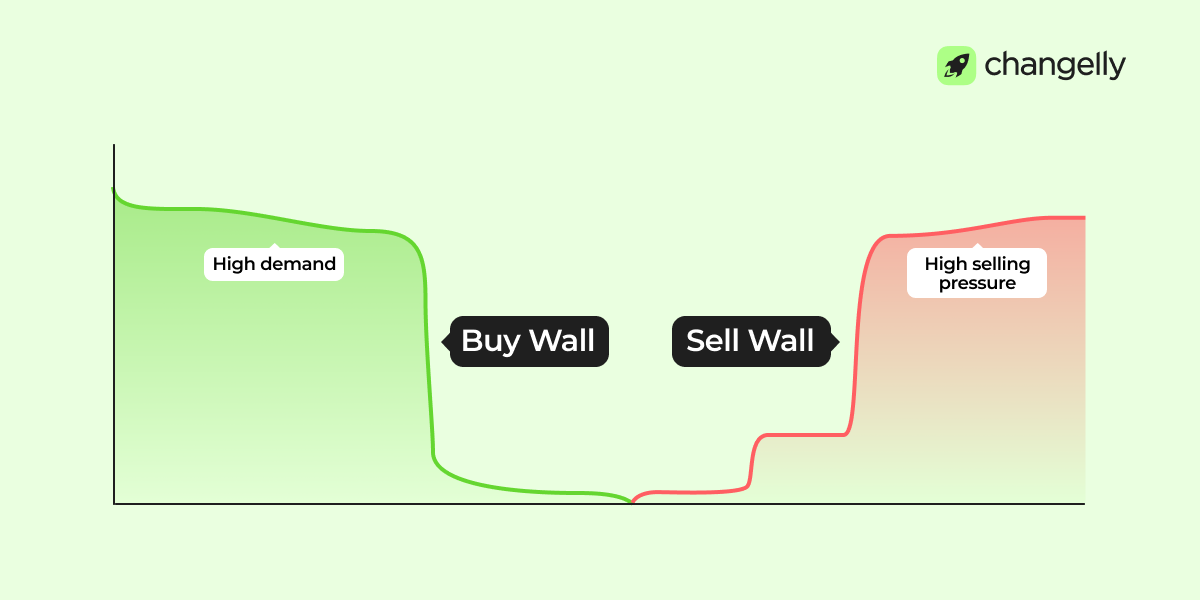
Depth Charts
A market depth chart shows the same order book visually. The green side displays total buy volume at each price; red shows sell volume. Sharp spikes or walls indicate strong support or resistance levels based on large order concentrations.
What Are Buy Walls and Sell Walls?
A buy wall forms when lots of buy orders stack at one price. It signals strong demand or support. A sell wall shows heavy selling interest, often acting as resistance. Both reflect trader sentiment and areas of low liquidity.
Types of Order Books
Centralized Order Book (COB)
A Centralized Order Book is managed by a single cryptocurrency exchange, like Binance, Kraken, or Coinbase. All user orders are stored and matched using the platform’s system.
These trading platforms offer fast execution, deep liquidity, and advanced tools. But you must trust the exchange to manage your funds and data.
Decentralized Order Book (DOB)
A Decentralized Order Book runs on a blockchain and isn’t controlled by a central authority. Projects like dYdX and Serum use smart contracts to match trades peer-to-peer.
You retain control of your assets, but execution may be slower due to network constraints. DOBs reflect the values of Web3 and DeFi.
Real-Time Order Book
A Real-Time Order Book updates instantly with every new order or trade. Most major platforms offer this by default. It shows live order book changes and helps you react quickly to price shifts and trading volume.
Aggregated Order Book
An Aggregated Order Book combines order book data from multiple trading platforms. It shows the best bids and asks across exchanges, offering broader liquidity and better price discovery.
Services like TradingView and CoinAPI provide this functionality.
Dark Pool Order Book
A Dark Pool Order Book hides order size and participant identity. It’s used mostly by institutions making large trades. These books don’t show up on public order books, but they influence market liquidity and price trends behind the scenes.
Types of Orders and How They Appear in the Order Book
Market Orders: Immediate Buying or Selling
Market orders execute instantly at the best available price. They don’t sit on the order book because they match existing orders right away. This is the fastest way to buy or sell, but not always the cheapest, especially in volatile markets or under rate limits. Beginners often use market orders for simplicity, but they offer less control over the final price.
Limit Orders: Setting Your Own Price
A limit order lets you set a specified price at which you want to buy or sell. It appears on the order book and waits until another trader accepts your offer. This gives you more control and is ideal when you’re targeting a specific price. It’s a smart choice for patient traders making strategic trading decisions.
Stop Orders: Trading When a Condition Is Met
Stop orders trigger only when the market hits a certain price. They become market orders or limit orders once activated. Many use them to stop losses or lock in gains automatically. To set these effectively, you’ll need to obtain data from the market and decide your risk level in advance.
How Orders Get Matched
Matching begins when a buy order offers to pay the same amount a sell order is asking. The system compares all prices in the book and looks for matches. It starts with the best price, then checks which order came first. That one gets filled. If the match isn’t exact—for example, if the buy order is larger than the sell—it only fills part of the order. The rest waits for another match. This process runs constantly, ensuring every price agreement results in a trade.
Some decentralized exchanges skip this system entirely. Instead of matching orders, they use AMMs (automated market makers) where traders swap tokens directly with a liquidity pool, not another user.
How Traders Use the Crypto Order Book
Traders read the order book to track supply and demand. They look at volume around key levels and watch how bid prices change in real time. A surge in bids may suggest strong demand, and possibly support. Traders place limit orders just above stacked bids to get filled early, or just below major asks to sell into resistance.
The goal isn’t to guess direction, but to see where pressure builds and use that info to plan entries, exits, or stop-loss levels.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
One mistake is misreading buy or sell walls as fixed. But those orders can disappear instantly. They show intention, not commitment.
Another mistake: ignoring historical data. Price reacts to the same zones again and again. If you don’t know where price bounced or stalled before, you’re trading blind.
Beginners also forget about assessing market sentiment. They react to a crowded order book without checking volume, price action, or recent news. If traders pull orders or volume dries up, sentiment has shifted. Emotional trades follow price, not logic. That leads to overtrading or chasing. And many ignore overall market conditions, thinking a local wall matters more than macro trends. Order books help, but only if read in context.

Final Words
Order books aren’t predictions, they’re rather windows into market intent. They show where people want to trade, not where the price will go. But used right, they help you see pressure, plan smarter entries, and avoid bad fills. Start small, test what you see, and match it with charts and volume. That’s how you learn to trade with real context, not noise.
FAQ
Can I trade without understanding the order book?
Yes, you can trade without using the order book, but you may miss important signals. It’s a critical component of any exchange that helps you make informed decisions. Without it, you’re just guessing. The book shows what buyers and sellers are doing in real time, which can help you choose better entry and exit points.
What is the purpose of an order book?
The order book is a critical component that shows all open buy and sell orders. It enables price discovery by letting traders compete on price. It also supports market liquidity, ensuring trades happen quickly. By watching the order book, you can gain valuable insights into demand, supply, and price momentum before making a move.
What happens when a bid matches an ask in an order book?
When a bid matches an ask, a trade is executed. This process is automatic and happens through the exchange’s matching system. The buyer gets the asset, and the seller receives payment. It’s how every crypto trade works. The matched price becomes part of price discovery, influencing the next market price shown on the platform. That’s why order books are so central to how exchanges operate.
How often does the order book update, and can I trust what I see?
The order book updates in real time, reflecting every new trade or order. You see real time market data, which helps you react to fast-moving conditions.
However, rate limits on your device or API might cause small delays. Also, traders can cancel orders, so market conditions may change quickly.
Still, the order book data is accurate and remains your best view into what’s happening now.
What does it mean if there’s a huge buy wall or sell wall?
A buy wall means many buy orders are stacked at one price. It suggests strong demand or support at that level. A sell wall shows lots of selling interest and acts as resistance. These walls shape market sentiment and signal where traders expect price to stall. Big walls can also indicate low liquidity above or below, affecting market depth and market liquidity overall.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.
The post What Is an Order Book in Cryptocurrency Trading? appeared first on Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly.


